Metabolic rewiring induced by ranolazine improves melanoma responses to targeted therapy and immunotherapy
A study led by Navarrabiomed proposes a therapeutic alternative to treat melanoma.
- The drug ranolazine, used to treat chronic angina pectoris, could improve response to anti-melanoma therapies.
- This is a multicenter investigation carried out by Navarrabiomed biomedical research center, the Institute for Neurosciences CSIC-UMH, and IRB Barcelona.
The prestigious journal Nature Metabolism has published the results of a study in mice that determined that ranolazine, a drug that is currently administered to patients to treat heart conditions, delays the appearance of resistance to melanoma treatments, by blocking fatty acids metabolism. This research has been led by Navarrabiomed, together with the Institute for Neurosciences (CSIC-UMH) and IRB Barcelona. Melanoma is the most aggressive type of skin cancer and, although it only accounts for 10% of skin cancer cases, it is responsible for 90% of deaths associated with skin tumours. Thanks to the development of targeted therapies and immunotherapies, the clinical management of patients affected with this type of cancer has improved, however, these therapies still have limitations because 50% of patients do not respond adequately and even develop resistance.
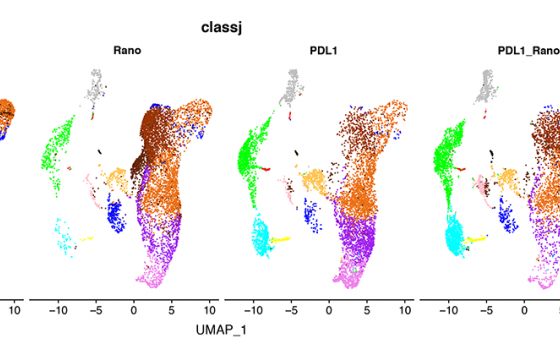
The evidence suggests that this resistance could be linked to metabolic reprogramming in cancer cells that is associated to changes in the way in which cells process and use nutrients. This research demonstrates that fatty acid metabolism plays an important role in the development of resistance to melanoma treatments.
Researchers have confirmed that increased fatty acid oxidation occurs during long-term treatment with BRAF inhibitors, one of the key genes in tumour progression, contributing to therapy resistance.
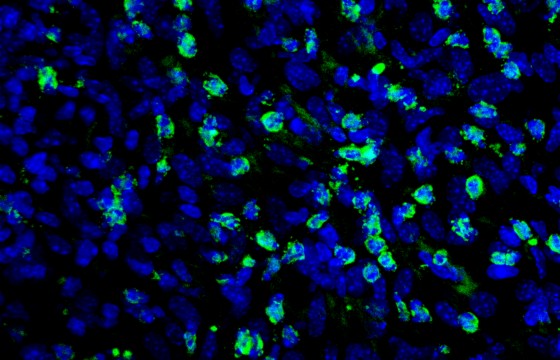
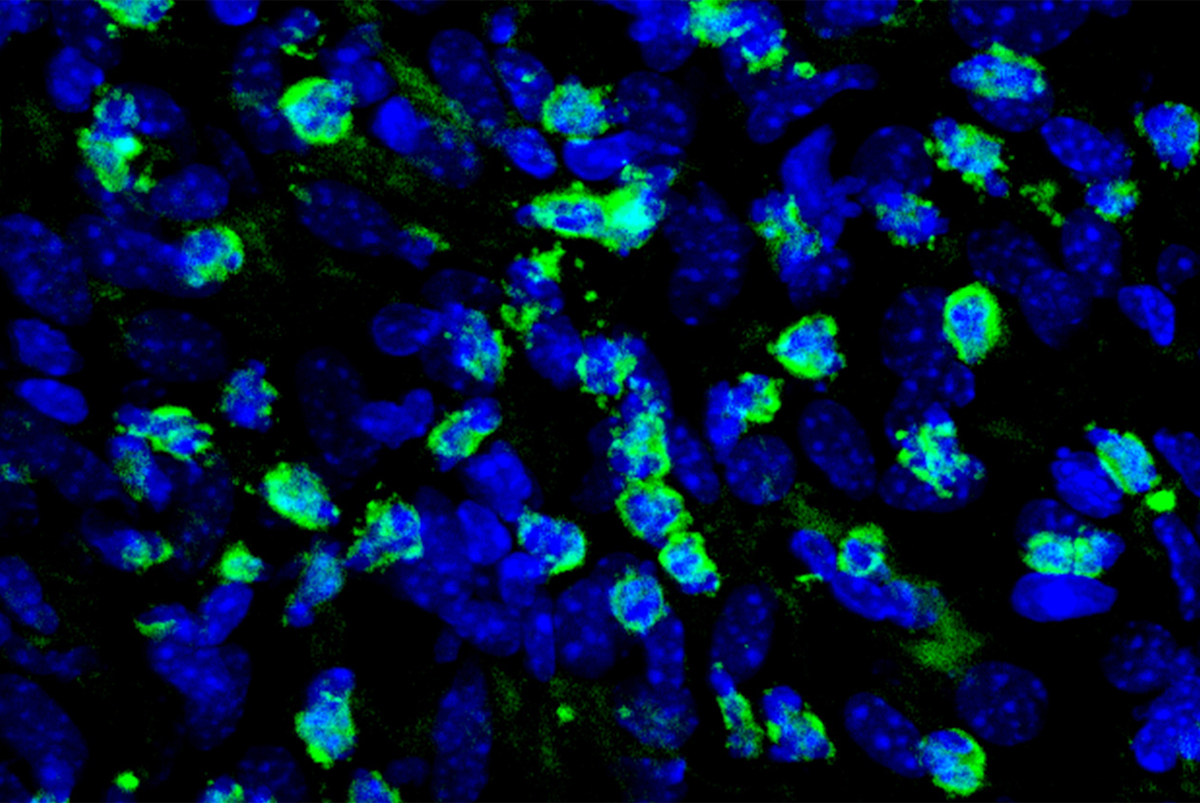
Ranolazine increases the efficacy of targeted therapy against melanoma because it can target fatty acid oxidation. In addition, the application of this drug promotes that melanoma cells become more visible to the immune system,improving the response to immunotherapies and increasing the ability of lymphocytes to control tumour growth.
A multicenter investigation
The Navarrabiomed Cancer Signaling Unit, directed by Imanol Arozarena Martinicorena, has coordinated the course of the research and has been in charge of carrying out the experiments related to resistance to targeted therapies and the study of how ranolazine affects the immunogenicity of melanoma cells.
Researchers at the laboratory led by Berta Sánchez-Laorden, belonging to the Cell Plasticity in Development and Disease group at the Institute for Neurosciences, have developed immunotherapy experiments in mice and have carried out the study of immune cells in the tumour microenvironment.
In addition, the IRB Barcelona Stem Cells and Cancer research group, led by Salvador Aznar-Benitah, has carried out individual cell RNA sequencing analyses, which have made it possible to find out in detail the effect of the drug on the state metabolism of tumour cells.
Funding
This study, which has been made possible thanks to funding granted by the Ministry of Science and Innovation, the Carlos III Health Institute, the Government of Navarra, the Spanish Multidisciplinary Melanoma Group (GEM), and the Melanoma Research Alliance, is a clear example of how basic research can contribute a lot to the repositioning of drugs, which makes it possible to significantly shorten the deadlines for providing answers to patients suffering from diseases as prevalent as cancer.